Samsung Display’s LEDoS (LED-on-silicon) technology for augmented reality (AR) device displays is expected to follow Blue + QDs →RGB 3-panel→Monolithic 1-panelMethod route evolution.
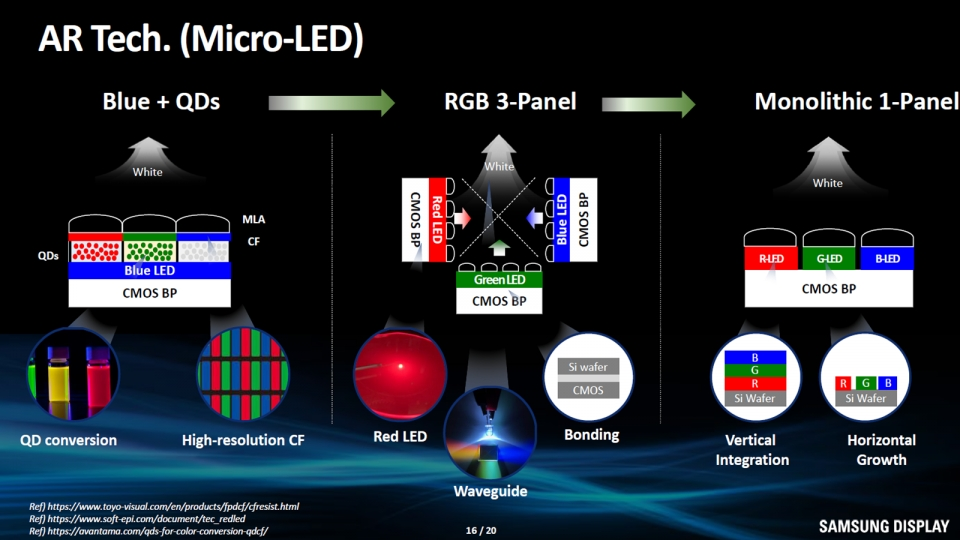
On May 23, Samsung Display Executive Director Jongmoo Heo introduced representative LEDos technologies: blue + quantum dot (QD) method, RGB 3-panel, Monolithic 1-panel.
LEDOS refers to the technology of forming micro light-emitting diodes (LEDs) of about a few microns (μm) on a silicon substrate. LEDos are expected to be used in augmented reality (AR) devices to display extended reality (XR) devices. This is because LEDs, which have an advantage in brightness, have an advantage in LEDos where information must be superimposed onto the real world.
Blue + QD LEDos are a method of forming blue LEDs on a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) substrate (backplane), and then realizing the color through a QD color conversion layer. A microlens array (MLA) is placed on top of the QDs to improve light extraction efficiency. MLA is also available for RGB 3-panel and Monolithic 1-panel LEDos.
The RGB 3-panel method is a technology that creates three panels by forming R, G, and B micro LEDs on three CMOS substrates. In this case, waveguide (optical waveguide) technology is required. Waveguide technology transmits images by controlling light and directing it in specific directions.
Monolithic 1-panel method has one panel. R, G and B LEDs are stacked vertically on a CMOS substrate or horizontally side by side on the same layer.

Samsung Display Executive Director Heo Jong-moo introduced LEDos technology including blue + quantum dot (QD) method, RGB 3-panel, Monolithic 1-panel
Managing Director Heo Jong-moo said: "Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) can achieve RGB by depositing on glass or CMOS substrates, but LEDs require high-temperature epitaxial processes, so RGB LEDs must be manufactured." Managing Director Heo said: Producing RGB LEDs or patterning them separately in each panel technology direction is a difficult process, which increases product costs. Of course, this is also a problem that must be overcome when developing high-resolution panels.
He said that XR display is not just an extension of the previously used OLED, but a comprehensive technology that can create new value in optics, panels, processes and materials.
The managing director of Heo pointed out that the virtual reality (VR) devices released so far have not yet established themselves in the market for the following reasons: lack of value such as content, inconvenience of the device, and high cost. So far, the VR equipment itself is not as comfortable as wearing glasses to see the screen in front of you, and the cost has exceeded the level of popularization.
Managing Director Heo added: The XR market will only grow significantly when the three elements of value, convenience and cost are present. Currently, the market is still in its infancy. Samsung Display has launched the "M Project" and will develop a microdisplay of about 1 inch by the end of 2022. OLEDoS and LEDoS both deposit OLED on a silicon substrate and are both representative micro-display technologies.
译自thelec
原文始发于微信公众号(MicroDisplay):Analysis of the evolution route of MicroLED microdisplay technology of Samsung Display XR Display


